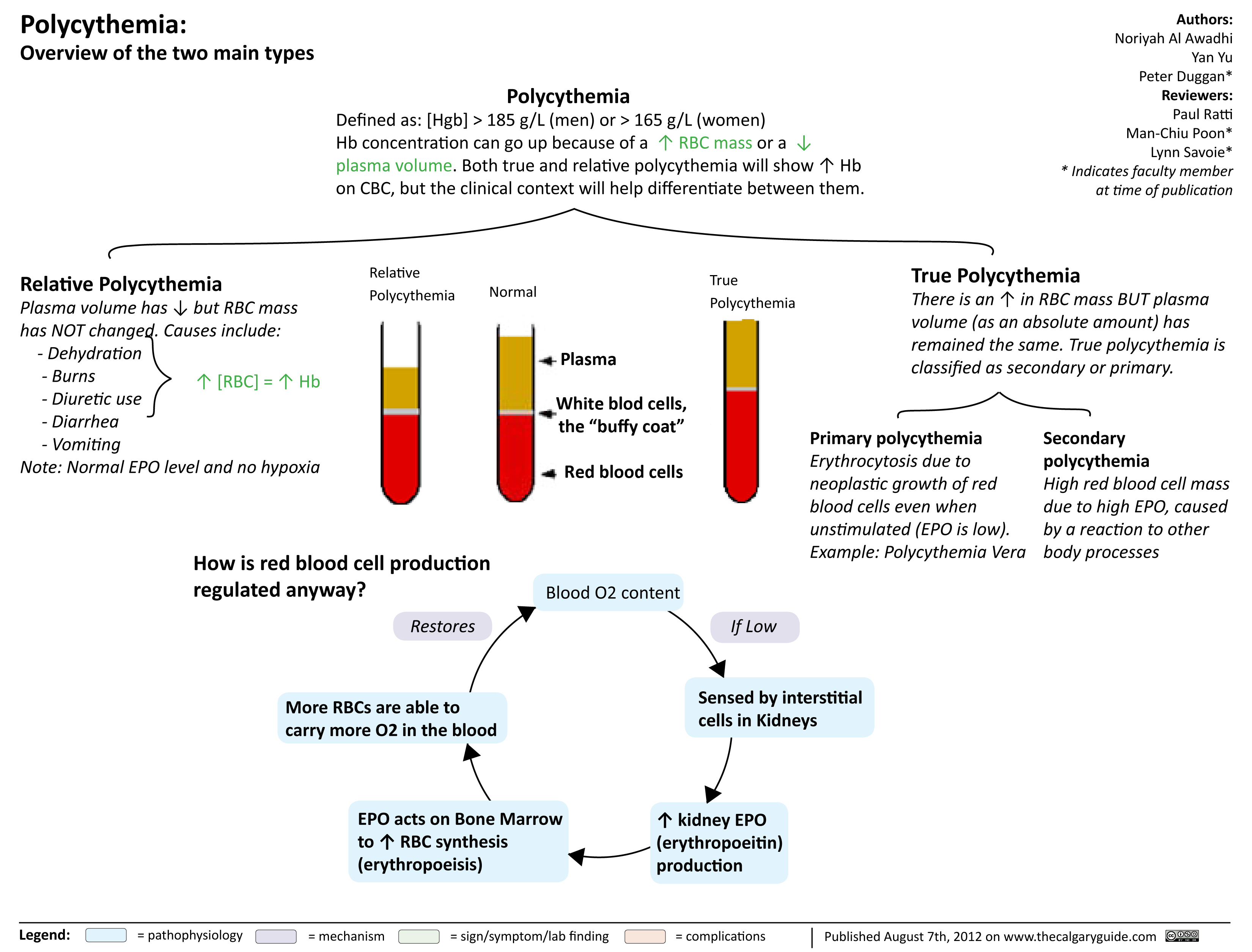
Polycythemia Overview Calgary Guide
More-specific symptoms of polycythemia vera include: Itchiness, especially after a warm bath or shower. Numbness, tingling, burning, or weakness in your hands, feet, arms or legs. A feeling of fullness soon after eating and bloating or pain in your left upper abdomen due to an enlarged spleen. Unusual bleeding, such as a nosebleed or bleeding gums.

Polycythemia Vera Stepwards
Polycythaemia vera (PV) is a type of blood cancer that affects the bone marrow. Bone marrow is where blood cells are made. In PV, the body makes too many red blood cells. This can make the blood thicker than normal. Some people with PV also have too many white blood cells and platelets in their blood. Having too many red blood cells increases.

Polycythemia Vera Treatment Guidelines Pregnant Center Informations
Polycythemia vera is a rare disease that causes excessive red blood cells to be produced and circulate in the body. The condition occurs during adulthood. The effects and prognosis can vary, and certain factors are associated with a worse prognosis—older age, a high white blood cell count, blood clots, and a genetic abnormality.

Polycythemia Vera A Comprehensive Approach to Management Hematology Advisor
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a relatively indolent myeloid neoplasm with median survival that exceeds 35 years in young patients, but its natural history might be interrupted by thrombotic, fibrotic, or leukemic events, with respective 20-year rates of 26%, 16%, and 4%. Current treatment strategies in PV have not been shown to prolong survival or.
What is Polycythemia Vera Causes, Symptoms, Diagnoses, Treatment, Life Expectancy HealthMD
Polycythemia vera is a chronic myeloproliferative neoplasm characterized by an increase in morphologically normal red cells (its hallmark), but also white cells and platelets. Ten to 15% of patients eventually develop myelofibrosis and bone marrow failure; acute leukemia occurs spontaneously in 1.0 to 2.5%. Untreated, there is an increased risk.

Polycythemia What Is It, How It Differs from Polycythemia Vera, and More Osmosis
FS13 Polycythemia Vera Facts I page 1 Revised April 2015 Causes The cause of PV is not fully understood. Almost all patients with PV have a mutation of the JAK2 (Janus kinase 2) gene. This mutated gene likely plays a role in the onset of PV.

Polycythemia Vera (PV) Calgary Guide
Die Polycythaemia Vera (PV) ist eine seltene Erkrankung der blutbildenden Zellen im Knochenmark, sie ist dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zu viele Blutzellen gebildet werden. Im Vordergrund steht die Überproduktion der roten Blutkörperchen (Erythrozyten), welche einer Entartung von Stammzellen im Knochenmark zuzuschreiben ist.
Polycythaemia Vera LearnHaem Haematology Made Simple
Die Polycythaemia vera ist eine chronische myeloproliferative Neoplasie, die sich durch eine Zunahme von morphologisch normalen Erythrozyten (sein Markenzeichen), aber auch weißen Zellen und Blutplättchen auszeichnet. 10 bis 15% der Patienten entwickeln schließlich eine Myelofibrose sowie Knochenmarksversagen; akute Leukämie tritt spontan bei 1,.

What Is Polycythemia Vera? PV Reporter
red skin, especially on the face. frequent nosebleeds. bleeding gums. easy bruising. ringing ears. blurred vision. a burning sensation on the skin, especially of the hands and feet. heavy bleeding.

Polycythemia Vera is a myeloproliferative disorder. Polycythemia vera, Mom health, Hematology
Die Polycythaemia vera ( PV) zählt zu den sogenannten klassischen chronischen myeloproliferativen Erkrankungen ( MPN) des Knochenmarks. Dazu gehören neben der PV die Essentielle Thrombozythämie ( ET ), die präfibrotische Primäre Myelofibrose (präPMF) und die Primäre Myelofibrose (PMF). Benennung

Polycythemia Vera Symptoms, Treatment & Lifestyle Changes NuvoVivo
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a relatively indolent myeloid neoplasm with median survival that exceeds 35 years in young patients, but its natural history might be interrupted by thrombotic, fibrotic.

Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia 2019 update on diagnosis, risk‐stratification
Der natürliche Krankheitsverlauf ist durch unterschiedliche Stadien gekennzeichnet. Charakteristisch ist eine anfängliche länger andauernde polyzythämische Phase mit zunehmender Splenomegalie und eine spätere sog. ‚Spent Phase' bzw. Phase der postpolycythaemischen Myelofibrose mit reduzierter Bildung von Blutzellen.
Polycythemia Vera Cause, Stages, Symptoms & Treatments
So können Sie Ihren Krankheitsverlauf online verfolgen und mit Ihrer Ärztin oder Ihrem Arzt besprechen. MPN-Tracker Wenn Sie Ihre Symptome schwarz auf weiß festhalten möchten, können Sie sie auch in unserem Symptomerfassungsbogen vermerken, ausdrucken und zum Arztbesuch mitbringen. GettyImages-697574745
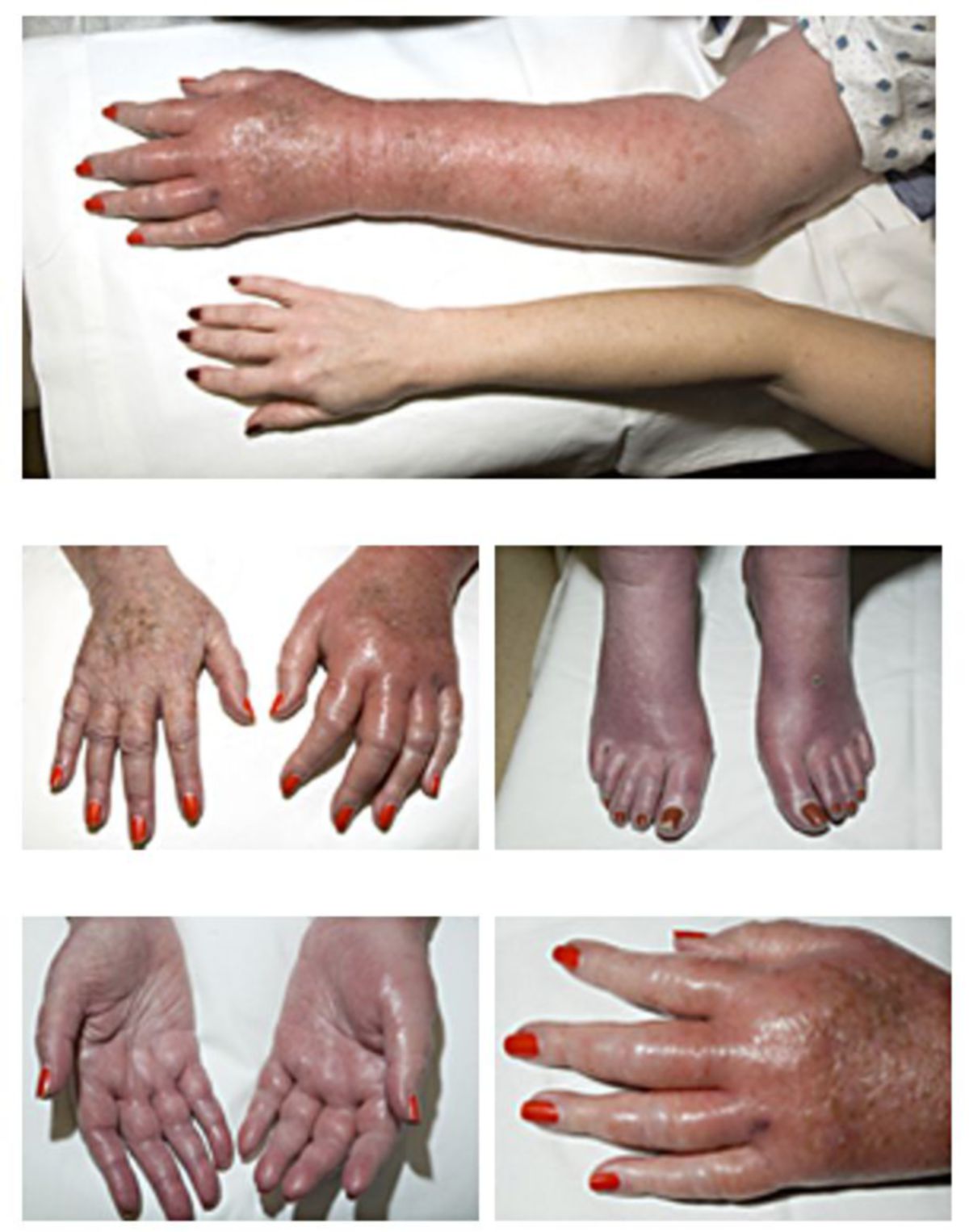
Polycythaemia vera DocCheck Flexikon
Die Polycythaemia vera ist eine myeloproliferative Neoplasie der blutbildenden Zellen im Knochenmark und führt zu einem Überschuss aller Arten von Blutkörperchen. Sie wird durch Mutationen des Januskinase-2- ( JAK2 -)Gens verursacht, wodurch ein Protein (Enzym) gebildet wird, das die Überproduktion von Blutkörperchen anregt.

Polycythemia Vera Causes, Symptoms, Cancer, Diagnosis, Treatment
Klinisch wird die Polycythämia vera in 2 Phasen unterteilt (WHO 2022): Chronische Phase (prä-polyzythämische und polyzythämische Phase): Überproduktion von Erythrozyten und damit einhergehend erhöhte Hämoglobin- und Hämatokrit-Werte Spätphase (Post-PV-Myelofibrose): Übergang der Erkrankung in eine sekundäre Myelofibrose

Understanding Polycythemia Vera MPN Cancer Connection
Die Polycythaemia vera ist eine seltene Krankheit, die im Lauf des Lebens erworben wird. Jährlich erkranken etwa 1.500 Menschen in Deutschland an einer Polycythaemia vera. Die Erkrankung trifft meistens ältere Menschen über 50 Jahre, kann aber auch bei Jüngeren auftreten.